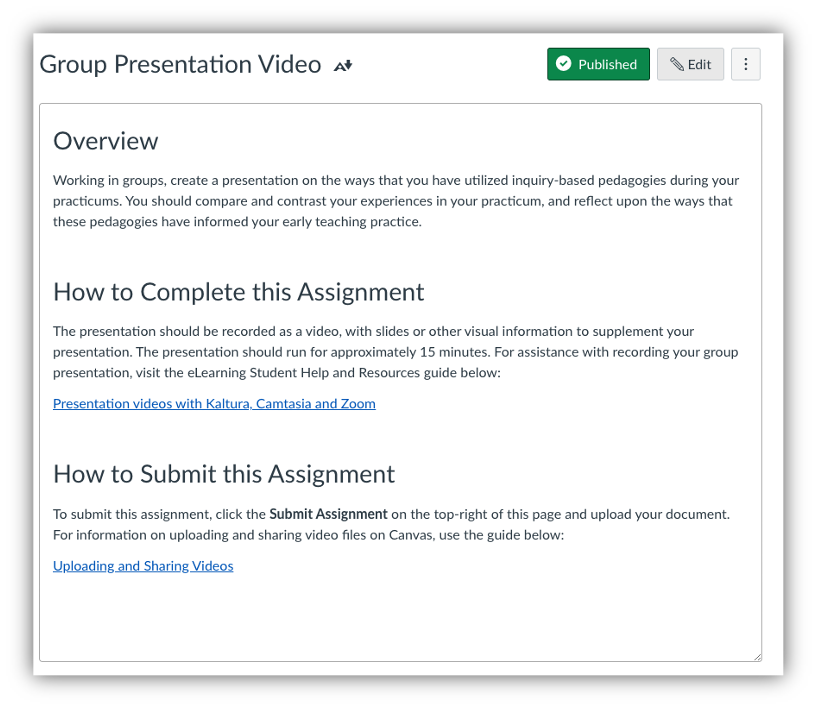
As students increasingly rely on their mobile devices to access course content, it is imperative to understand how to structure and design a Canvas course so that students have easy and accessible access to course content through a computer interface and the mobile app.
Wayfinding
When providing wayfinding instructions, use language that is neutral enough to work on both the computer interface and the mobile app, for example:
“Click the Syllabus button on the left”
-VS-
“Select ‘Syllabus’ from the course navigation”
Front Load Content
Ensure that vital information within a page or assignment description is presented first so less scrolling is required. Integrate images intentionally to avoid slow load times. If images are used, integrate them towards the bottom of the page to eliminate slow load times and space for scrolling.
Integrate White Space
White space is an area intentionally left untouched on a page and often appears between figures, text, columns, and images (etc.). A simple page layout with ample white space can positively impact viewer engagement, heighten readability and organization, decrease overwhelm and distraction, and reduce clutter. There is no single formula for integrating white space, but tips to guide integration are to integrate white space between images and between paragraphs, use consistent line spacing throughout, group information using bullets and headings, and remove unnecessary graphics and images.
Design for Touch
The primary mode of interaction on mobile devices is typically a touch screen. For items such as links that require an action like clicking, ensure that there is enough space between each link to avoid accidental clicking. When providing multiple links on one page, instead of placing links next to each other horizontally, stack them vertically with ample white space between them to avoid accidental clicks.
Chunk your Content
To heighten organization and decrease overwhelm, rather than place all content on one page, separate your content over several pages. For instance, use Modules to organize content into a table of contents. Rather than have all Week 1 content in the Week 1 overview, split the content into multiple sections: Week 1 Overview; Week 1 Readings; Week 1 Assignments.
Drop Cap
To add a more visual style of representation to your paragraphs, while maintaining design accessibility on the mobile app, you may decide to incorporate drop caps. Drop caps are large capital letters that extend below the baseline of the first line of an opening paragraph. Canvas indents the text below the first line to make room for the drop caps. You can format drop caps in HTML for any selected paragraphs to add a decorative component.
<p><span style="float: left; width: 0.7em; font-size: 400%; font-family: algerian, courier; line-height: 80%;">I</span>n 2022, We all saw...</p>
Video
To create a video, you can record using the built-in camera on your mobile device (iPad, iPhone, Android Phone) and then upload the video to Kaltura.
When creating a video be sure to hold the mobile device in a horizontal position. Holding the mobile device in a vertical position will reduce the size of the image when uploaded to Studio, causing the video to display with two vertical black bars on the sides.
Upload your videos or media files to Kaltura and then insert them into Canvas. Add captions using Kaltura.
Use Text Headers
Use text headers rather than indentations to organize your course. Indentations will not be seen on Canvas mobile. Instead, it is recommended to add text headers to organize your content and to support students to navigate the course. Use the styles built into Canvas because they will correspond to style definitions specific to the mobile apps, which also heightens accessibility.
To add a text header, press the plus sign in a module and choose text header. Use a consistent naming scheme. Refer to the Canvas Community guide on how to add a text header as a module item.
Present Content with Canvas Pages
When possible, use Canvas pages to create content rather than word documents and PowerPoint presentations. Canvas pages are much easier for students to read in the Canvas student app, especially if you have a document with multiple links because the links will be easier to select on a Canvas page.
Keep the Instruction Platform Neutral
You likely won’t know if your students are using Canvas on their desktop computer or their mobile devices and so it is best to keep any directions or instructions neutral to avoid student confusion. Avoid using instructions that include specific directions for one platform. Instead, your assignment instructions should include neutral guides for all platforms.
Test your Course
Be sure to test your course content on a mobile device to identify potential access issues and to discover which instructional tools are not compatible with mobile (Java-based, some publisher platforms, etc.). If you must use a function or tool that is not fully supported in mobile, make note of it and let your students know.